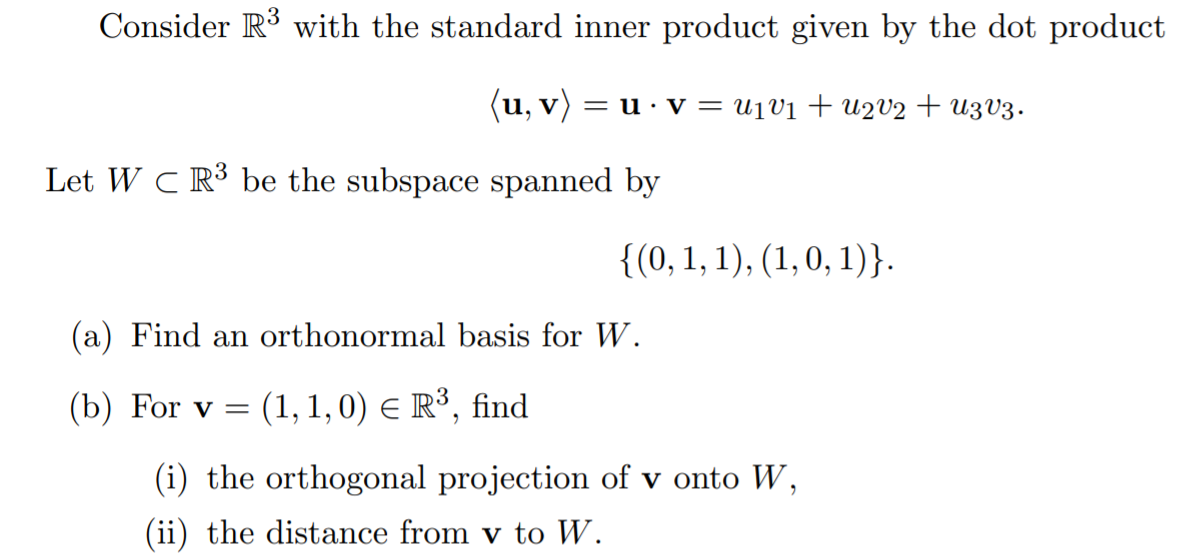
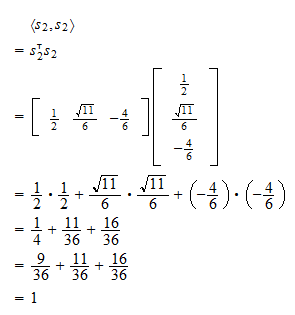Solved! -63) e1, e2, e3 0 Using the Hermitian inner product to define distances and angles, answer: a)Are they an orthogonal basis? b) Are they an orthonormal basis? c) Find
![SOLVED: (7 marks:) Let C[0, 1] have the inner product defined by (f,g) = J" f()g(w)d, Vf,g e C[o, 1]. Let U = spanx 1, x + 1, x + x2 be SOLVED: (7 marks:) Let C[0, 1] have the inner product defined by (f,g) = J" f()g(w)d, Vf,g e C[o, 1]. Let U = spanx 1, x + 1, x + x2 be](https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_images/21ea14407f054866b063a2db39f5d097.jpg)
SOLVED: (7 marks:) Let C[0, 1] have the inner product defined by (f,g) = J" f()g(w)d, Vf,g e C[o, 1]. Let U = spanx 1, x + 1, x + x2 be

linear algebra - For any inner product, can we always find a symmetric orthonormal basis? - Mathematics Stack Exchange

Lecture 11 Inner Product Spaces Last Time Change of Basis (Cont.) Length and Dot Product in R n Inner Product Spaces Elementary Linear Algebra R. Larsen. - ppt download

Inner Product Spaces Euclidean n-space: Euclidean n-space: vector lengthdot productEuclidean n-space R n was defined to be the set of all ordered. - ppt download

linear algebra - For any inner product, can we always find a symmetric orthonormal basis? - Mathematics Stack Exchange
The Fourier Transform • Introduction • Orthonormal bases for R – Inner product – Length – Orthogonality – Change of

Gram Schmidt Theorem - Every finite dimensional inner product has an orthonormal basis - lesson 16 - YouTube

SOLVED:Find an orthogonal basis and an orthonormal basis for the subspace W of 𝐂^3 spanned by u1=(1, i, 1) and u2=(1+i, 0,2).
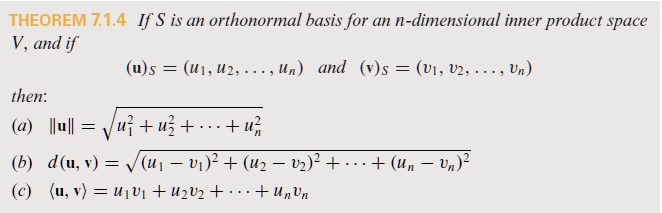
SOLVED: THEOREM 7.1.4 If S is an orthonormal basis for an n-dimensional inner product space V, and if (u)s = (W; U2. Un) and ()s = (V; U2, Un ) then: (a)

Gram Schmidts # Every finite dimensional inner product space has an orthonormal set as a basis - YouTube

Lecture 11 Inner Product Space Last Time - Coordinates and Change of Basis - Applications - Length and Dot Product in R n Elementary Linear Algebra R. - ppt download